Control PWM hardware from C
-
Hello,
I would like to know if there are libraries available (or drivers) to control the PWM hardware from C language? If so can you please let me know how to get it and how to use it please?
Thanks
-
@nsmith The easiest way to control PWM is using sysfs, if you look at the docs you can see the process is simpy to write to the control files.
https://docs.onion.io/omega2-docs/generating-pwm-signals.html
-
@nsmith Some sample code:
#include "include/motor.hpp" #include "include/gpiomux.h" #include "include/uciutils.h" #include "include/common.hpp" #include <string> #include <math.h> #include <syslog.h> Motor::Motor(char *uci_path, int max_move_time = 0){ // null the callbacks so we can check if they have been set _moving_call_back = NULL; _stop_call_back = NULL; _forward_call_back = NULL; _reverse_call_back = NULL; _max_move_time = max_move_time; init(uci_path); } int Motor::init(char *uci_path){ _pwm_channel = get_uci_path_int(uci_path, UCI_OPTION_MOTOR_PWM, STD_MOTOR_PWM_CHANNEL); _freq = get_uci_path_int(uci_path, UCI_OPTION_MOTOR_FREQ, STD_MOTOR_FREQ); _forward_duty = get_uci_path_int(uci_path, UCI_OPTION_MOTOR_FORWARD_DUTY, STD_FORWARD_DUTY); _reverse_duty = get_uci_path_int(uci_path, UCI_OPTION_MOTOR_REVERSE_DUTY, STD_REVERSE_DUTY); _stop = get_uci_path_int(uci_path, UCI_OPTION_MOTOR_STOP_DUTY, STD_MOTOR_STOP_DUTY); if (get_uci_path_int(uci_path, OPTION_MOTOR_DISABLED, 0)==1){ _config_disabled = true; _disabled = true; syslog(LOG_NOTICE,"%s is disabled", uci_path); } else { // some pins need to be set to GPIO mode if they are muxed. gpiomux_mmap_open(); std::string pwm = "pwm" + std::to_string(_pwm_channel); int mux_result = gpiomux_set(const_cast<char*>(pwm.c_str()), "pwm"); syslog(LOG_DEBUG, "GPIO Mux returned %d", mux_result); gpiomux_mmap_close(); openPwm(); } } int Motor::stop(){ if (isDisabled()==true) return EXIT_FAILURE; _is_moving = false; if (_stop_call_back!=NULL) _stop_call_back(_is_moving); setPwm(_stop); syslog(LOG_DEBUG,"Motor Stop"); } int Motor::forward(bool autostop = false){ if (isDisabled()==true) return EXIT_FAILURE; _is_moving = true; if (_forward_call_back!=NULL) _forward_call_back(_is_moving); setPwm(_forward_duty); if(_max_move_time > 0 && autostop == true) { sleep(_max_move_time); stop(); } } int Motor::reverse(bool autostop = false){ if (isDisabled()==true) return EXIT_FAILURE; //syslog(LOG_DEBUG,"Motor Reverse"); _is_moving = true; if (_reverse_call_back!=NULL) _reverse_call_back(_is_moving); setPwm(_reverse_duty); if(_max_move_time > 0 && autostop == true) { sleep(_max_move_time); stop(); } } int Motor::setPwm(int duty){ if (isDisabled()==true) return EXIT_FAILURE; float period = ( 1.0 / _freq ) * 1000000000; float pulseWidth = (period * duty) / 100; int iPeriod = round(period); int iPulseWidth = round(pulseWidth); std::string periodFileName = std::string(PWM_MAIN_DIRECTORY) + std::string("pwm") + std::to_string(_pwm_channel) + std::string("/period"); std::string dutyFileName = std::string(PWM_MAIN_DIRECTORY) + std::string("pwm") + std::to_string(_pwm_channel) + std::string("/duty_cycle"); std::string enableFileName = std::string(PWM_MAIN_DIRECTORY) + std::string("pwm") + std::to_string(_pwm_channel) + std::string("/enable"); FILE *fp = fopen(periodFileName.c_str(), "w"); if (fp == NULL) return EXIT_FAILURE; fprintf(fp, "%d", iPeriod); fclose(fp); fp = fopen(dutyFileName.c_str(), "w"); if (fp == NULL) return EXIT_FAILURE; fprintf(fp, "%d", iPulseWidth); fclose(fp); fp = fopen(enableFileName.c_str(), "w"); if (fp == NULL) return EXIT_FAILURE; fprintf(fp, "%d", 1); fclose(fp); } Motor::~Motor(){ closePwm(); } int Motor::openPwm(){ FILE *fp = fopen(PWM_EXPORT_FILE, "w"); if (fp == NULL) return EXIT_FAILURE; fprintf(fp, "%d", _pwm_channel); fclose(fp); } int Motor::closePwm(){ stop(); FILE *fp = fopen(PWM_UNEXPORT_FILE, "w"); if (fp == NULL) return EXIT_FAILURE; fprintf(fp, "%d", _pwm_channel); fclose(fp); } void Motor::enable(){ // in case we disabled the motor for emergency stop, // check we don't enable it if the configuration // says it disabled. if (_config_disabled == true) return; syslog(LOG_DEBUG, "Motor Enabled"); _disabled = false; } void Motor::disable(){ if (_disabled==false) syslog(LOG_DEBUG, "Motor Disabled"); if (_is_moving == true) stop(); _disabled = true; _is_moving = false; }
-
Thanks for that.
Does anybody know where i can find the source code for the command line program to control the pwm:
"onion pwm ....."
it should be in the docker file for the opwnWRT that is used to build the firmware image.
Anybody knows what path the source code for that command is in?
Thanks
-
@nsmith It's a script. /usr/bin/onion
-
@nsmith yep, @crispyoz is correct, that's where the script is installed on the device
We keep the source code on github: https://github.com/OnionIoT/Onion-Scripts/blob/master/onion.sh
-
Hello, thanks for the info.
So the website says this:
For GPIO18:
omega2-ctrl gpiomux set pwm0 pwm
For GPIO19:
omega2-ctrl gpiomux set pwm1 pwm
For GPIO20:
omega2-ctrl gpiomux set uart2 pwm23
For GPIO21:
omega2-ctrl gpiomux set uart2 pwm23
I notice that for GPIO 20 and 21 it has the same command above, is that correct?
omega2-ctrl gpiomux set uart2 pwm23
Thanks
-
@nsmith said in Control PWM hardware from C:
I notice that for GPIO 20 and 21 it has the same command above, is that correct?
Yes, the muxing of GPIOs 20 and 21 is controlled by a single command.
These pins can be regular GPIOs, serial UART2, or PWM channels. They're controlled together since UARTs are always 2 pins.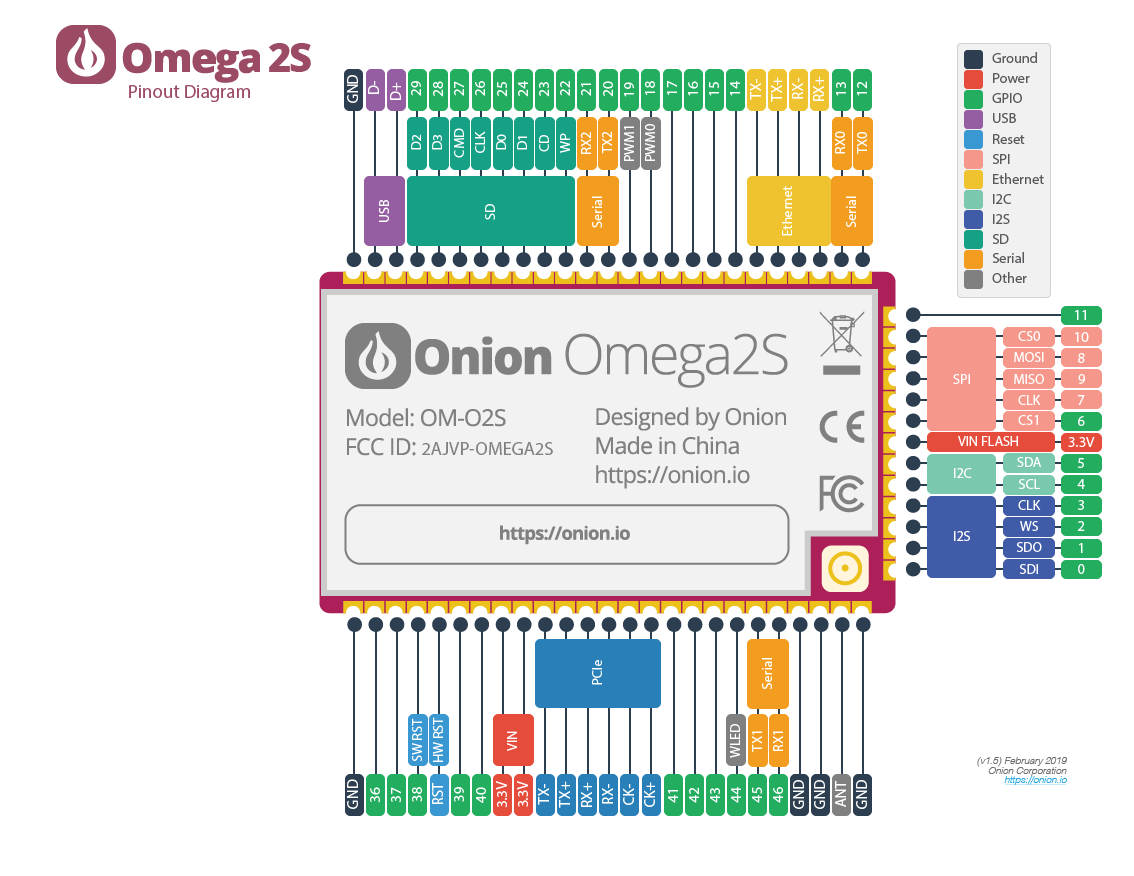
Because of this, you'll only need to run
omega2-ctrl gpiomux set uart2 pwm23once and both GPIO 20 and 21 will be set to PWM.